January 23, 1896: The First Public X-Rays
Subscribe! Spotify | RSS | More
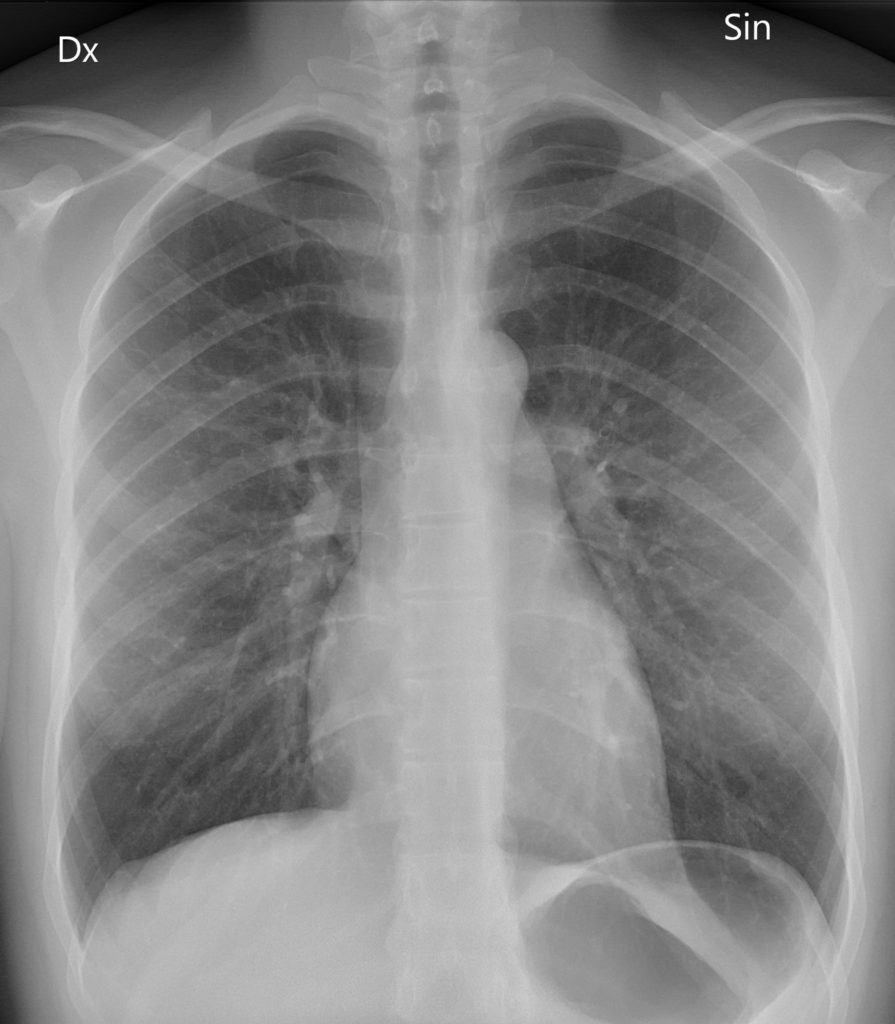
1896 – Although he was not the only person to be working on the technology and not the first X-ray, Wilhelm Roentgen gave the first public lecture and demonstration of his device. He photographed Dr. Albert von Kolliker’s hand at the Wurzburg Physical Medical Society.
The first X-ray he ever took was of his wife’s hand (with wedding ring on). The practice is also known as Röntgen rays.

Subscribe to Day In Tech History:
RSS Feed - iTunes - Android - Spotify - iHeartRadio
Facebook -
- RSS Bandwidth by Cachefly Get a 14 Day Trial
- Join me on Patreon and support Day in Tech History
- Sega and Bandai announce a merger
- Apple releases Macintosh Office
- The integrated circuit is conceived
- Lenovo acquired IBM ‘s Server division












![HP41c[1] HP41c[1]](https://dayintechhistory.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/10/HP41c1-340x250.jpg)




